
What is contract management by definition?
In the literature and on the Internet, you will find a wide variety of explanations, which are often based on the article on contract management in the German-language Wikipedia, which also provides various definitions:
- Contract management includes the supervision of contractual negotiations between client and contractor, implementation of contracts and making changes to contracts for technical, scheduling, personnel or financial reasons.
- Contract management refers to all activities within the scope of project management that deal with the development, administration, adaptation, processing and updating of all contracts within the scope of a project.
- In practice, contract management is regarded as the foundation for a company's business activities and therefore represents both a global and a complex corporate task.
- Contract management tasks
- Analog versus digital contract management
- Integration for contract management
- Contract management as a global task
- Practical check contract management
- Contract management and Compliance
- Contract management as project management?
- Contract management in the future
- Which contract management software is the right?
- Contract management software: smartLCM
These definitions can be summarized into the following core statements:
- Contracts are the starting point and the basis for business and legal actions in organizations and specialist departments. Internal and decentralized decision-making levels require direct access to the company's global information with disclosure of any risks.
- Successful and legally compliant management of these challenges requires concrete solutions aimed at identifying and effectively controlling risks, optimizing processes, and achieving efficiency gains and the necessary audit compliance in the area of contract management.
- Contract management refers to all activities within the scope of project management that deal with the development, administration, adaptation, processing and updating of the entirety of all contracts within the scope of a project.
Contract management tasks
- Preparation of draft contracts and agreements: Drafting, reviewing and finalizing contracts in collaboration with relevant parties and groups.
- Contract Negotiation: initiate negotiations with suppliers, customers or partners to achieve mutually beneficial terms.
- Monitoring of deadlines: continuous monitoring of contract performance to ensure compliance with terms and deadlines.
- Deadline monitoring
- Liquidity planning
- Risk assessment: Identify and evaluate potential risks associated with contracts and develop mitigation strategies.
- Contract performance
- Contract Renewal or Termination: Managing the renewal or termination process
- Change management: managing changes to contract scope, terms, or conditions, including contract amendments or modifications.
- Archiving
Objectives in contract management
The aim of contract management is to manage contracts as well as controlling and correct archiving. However, it is not just simple contract management but also includes the preparation of data, for example in the form of an analysis with risk assessment of existing and/or future contracts. Contract management can be implemented analogously using (paper) files or can be fully or partially digitized.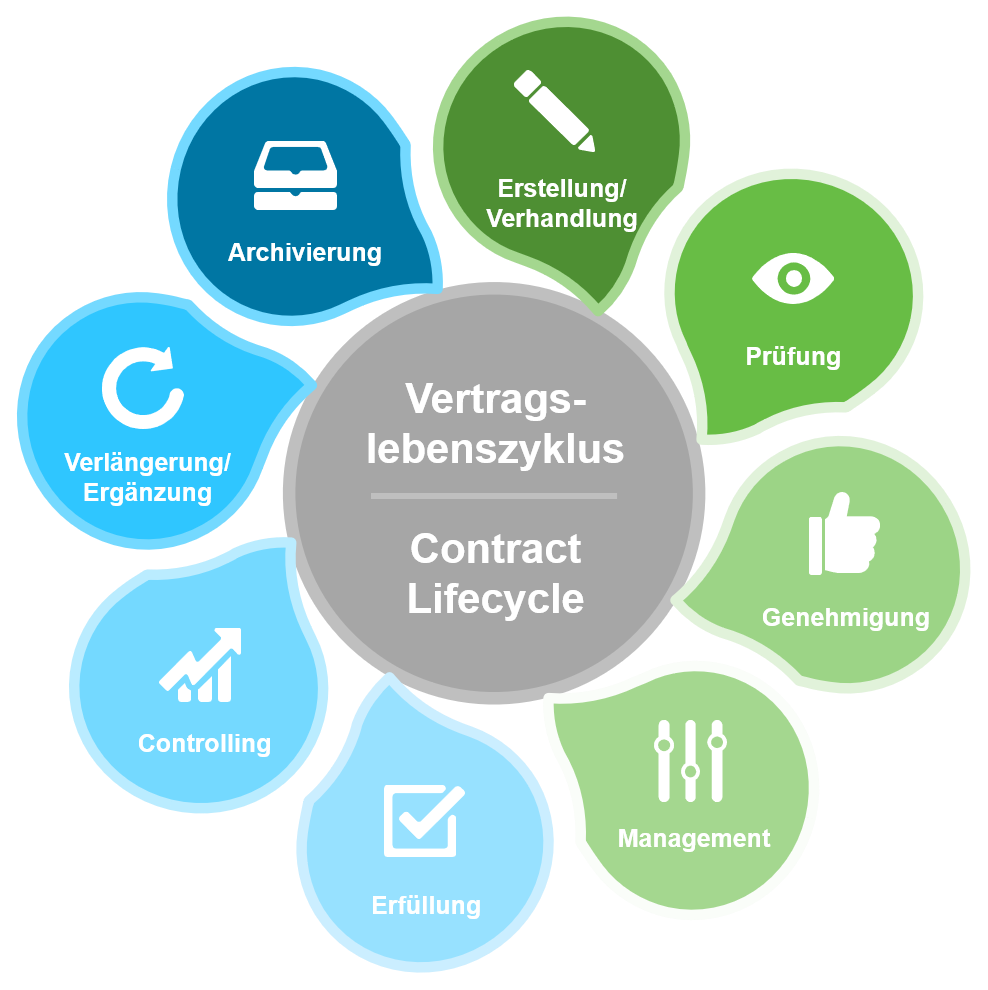
Figure 2: Digital contract management mapped in contract lifecycle
- Creation/negotiation
- Review
- Approval
- Management
- Fulfillment
- Controlling
- Extension/ Supplementation
- Archiving
Analog versus digital contract management
Contracts can be managed both analog and digitally (or a mixture of both methods).However, analog (traditional) contract management has some disadvantages compared to digital contract management. For example, the processing time is often longer with the analog method, partly because collaboration between several employees is only possible to a limited extent. In addition, it is often more difficult to access the documents and the contracts have to be filed and physically archived, which leads to increased space requirements. In addition to the difficulty of finding documents, there is also the risk of losing them. A (digital) analysis of contract management is hardly possible as the data is only available in its analog form. Conclusion on analog contract management: Efficient and secure contract management is hardly possible with analog contract management.
A software for contract management enables:- Overview of all recorded contracts
- Avoidance of missed deadlines such as revocation, term and termination periods
- Establish responsibility(s) of contracts beyond doubt
- Avoid the risk of lost contracts
- Complete integration into the business process
Conclusion on digital contract management: Continuous and efficient management of all contracts is therefore almost always only guaranteed with the digitalization of contract management using software.
API interfaces for effective contract management
However, the greatest advantages in digital contract management can be achieved by linking systems and processes (that already exist and are maintained in the company) via an API interface. The workflow is greatly simplified, errors are easy to detect and evaluations and analyses that were previously not possible can now be carried out across all systems.
Integration examples in contract management
Efficient storage, search and management of contract documents
ERP systems
More accurate and faster resource planning
Store signed contracts directly in the system. Speeds up the approval process
Ensures that contracts comply with legal requirements. Automated monitoring systems can generate alerts
Automatic processing of invoices, payments and other financial transactions
Direct communication and notifications in connection with contract changes or reminders
Why is contract management a global company task in modern and successful companies?
After the economic and financial crisis, conclusions about values and morals are being recast. The "honourable businessman" is (unfortunately) a thing of the past. Compliance is no longer a foreign word or a trivial offence.
"Sustainability has the right of way" or "How trust arises from understanding" - these or similar slogans are platitudes in today's world that revive more than ever claims from days long gone.
Thus, the contract as the foundation for business management in an organisation or company is not an "old" relic. Rather, according to textbook thinking, almost every business decision is based on a contractual agreement or leads to such an agreement. Thus, experts agree, a contract goes through a life cycle within a systematic process, modernly also called life cycle management, in which contracts with legal effect are designed, created, put into effect, managed, monitored, evaluated, terminated and archived.
Contract management in transition grows with the understanding of the topic of compliance - secure action in the company interprets itself in
- Yesterday, contracts were managed - mostly in folders and cabinets.
- Today we manage contracts - file, search and retrieve contracts electronically.
- Tomorrow we will understand contracts qualitatively within compliance, secure them and use them successfully.
Practical check contract management
What does that mean? A practical check of how companies have managed to successfully integrate their contract management as a global organizational task into their day-to-day business. Our practical examples show how the contract life cycle has been secured across departments through conscious responsibility throughout the entire organization in accordance with legal requirements (GoBD) and the company's own compliance and risk management and how it has been successfully implemented in contract management.
Organization Performance Quotient (OPQ)
The Organization Performance Quotient (OPQ) is an objective, universal and overarching value for measuring quality and compliance in the organizational areas and administrative processes in the penetration of global organizational tasks (e.g. contract management, risk/compliance management, BPM, etc.) and is a central element of the "Capture" phase in the phase model of the Organization and Process Handbook (OPH) method, as it provides valuable suggestions, discussions and information about the organization and the motivation of employees.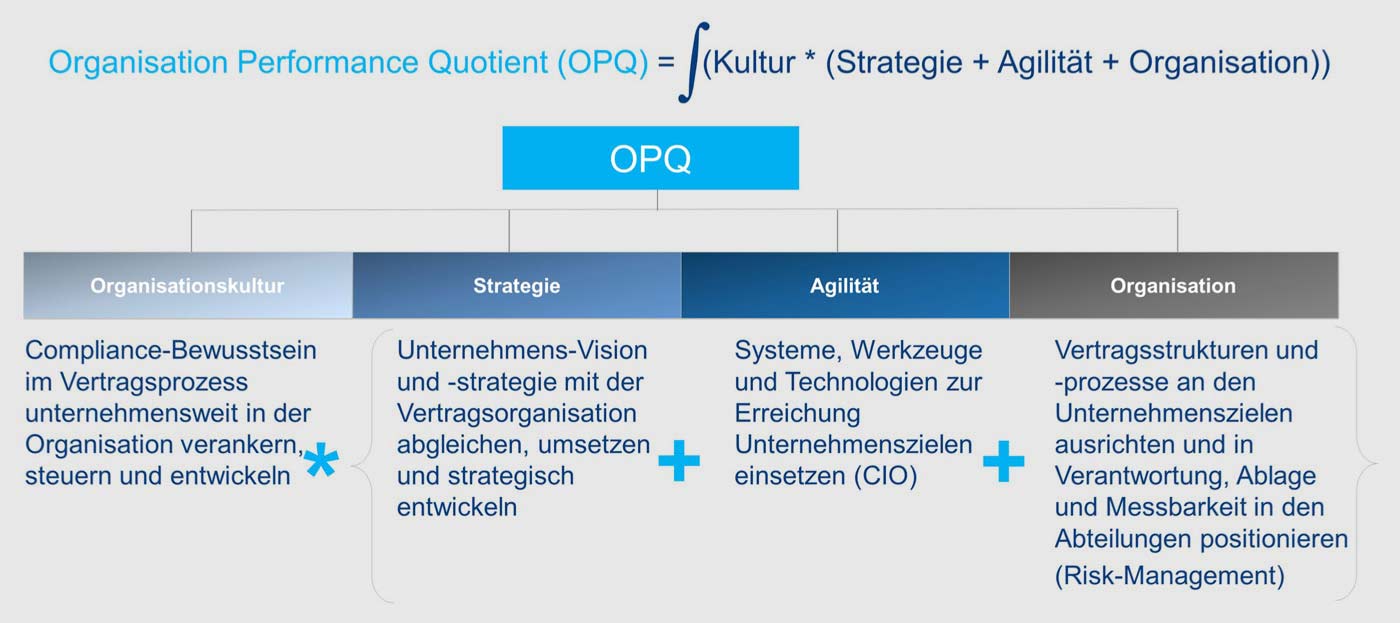
How does contract management support your compliance in the long term?
The aim of effective compliance management is to adhere to legal requirements and internal guidelines. By integrating contract management into compliance management, the prescribed requirements can be met.
A considerable proportion of documents and knowledge still exists in unstructured texts and files. The need for contract management software to ensure transparency and comply with obligations is therefore considerable. Deadlines and dates are stored centrally and can be accessed in the compliance area. Automated checks can also be carried out and monitored in accordance with current regulations. The result is a considerable minimization of risk.
Structured information and knowledge management in the area of compliance helps companies, even beyond departmental boundaries.
How can contract management be understood as project management?
There are approaches and solutions for this that are described as a method in Enterprise Information Management (EIM). In order to treat contract management like a project, the departments responsible for the contracts must give up the idea that the IT solution can solve all problems itself. Instead, the aim is to develop the business process in a structured way, not through IT, but together with IT.
The following phases must be described, implemented and monitored for the project:
- Capture – phase for describing and recognizing the actual state
- Discover- phase to define the objectives and potentials
- Improve – phase with argumentation and describing the process model
- Score – phase as strategic reasoning and measurability of future processes
With the help of these phases, a company achieves
- The measurability of steps and changes according to a continuous improvement process (CIP)
- Sustainable documentation of processes and procedures actually put into pratice in the departments
- Implementation of projects according to the principle "InTime, InQuality, InBudget"
Contract management in the future
The future of contract management is exciting. This is strongly characterized by an even more pronounced digitization of the entire contract lifecycle.
The automation of all processes will be the goal of many companies in order to minimize the effort and the associated costs. Artificial intelligence (AI) will also play a significant role in the desired increase in efficiency. AI can be used, for example, to point out dangers and errors in contracts before they are signed. Suggestions for a change of contract in order to achieve better conditions would also be possible.
Other future topics in contract management include the use of blockchain technology. This technology is decentralized in nature. It is no longer possible to change the contract after the fact, thus protecting against disputes and attempts to manipulate the content of the contract.
Which contract management software is right for my company?
Choosing the right contract management software is only guaranteed with a thorough needs analysis. The requirements depend heavily on the industry, the country in which the company is active and the company itself:
- Functionality requirements (specific requirements)
Every company is unique in its need for the required functionalities of contract management software. The functions range from very specialised and complex to very general and simple. - Security: Regular and timely security/updates
System and data security is very important to prevent data theft or loss. It is therefore essential to ensure regular updates. These updates must also be implemented promptly to ensure the stability and integrity of the software - Budget
It is important to determine the costs for the introduction/expansion of the contract software in advance so that these are within the estimated budget. - Integration capability
The integration of other digital systems and (third-party) software is an important factor when selecting a contract management system. Integration enables users to work in their familiar environment. In addition, the database does not have to be migrated. Data can often only be stored and displayed in a system in this way; a complete replication of the functions, for example, would be too costly and time-consuming. - Support
What kind of support, to what extent and what processing time can be expected? Acute errors and questions often require a very prompt solution.
Our contract managemente software: smartLCM Contract Management
With the contract management software smartLCM Contract Management you manage all tasks of contract management, digital, simple and transparent.
smartLCM contract management has been one of the leading software in matter and contract management for more than 20 years: a powerful contract management tool for your measurable success and the basis for transparent and secure information processes.
The basic functions of modern contract management software are contract administration, contract controlling and deadline monitoring. The IT integration into existing ERP, CRM or other information systems can be easily carried out within the project by means of standards such as CMIS - Interface or SAP Integration Gateways.
No matter whether as a single workstation or as a global enterprise application: smartLCM contract management can be used across multiple locations.
